Product Overview
shERWOOD shRNA Design + Optimized shRNA Processing = Superior Knockdown
shERWOOD-UltramiR shRNA reagents are next generation vector-based RNAi triggers designed using the proprietary shERWOOD algorithm developed and validated in Dr. Gregory Hannon’s laboratory at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (Knott et al 2014). An alternate microRNA scaffold “UltramiR” has been optimized for increased shRNA processing and potency based on new information on the key determinants for primary microRNA processing (Auyeung et al 2013).
The shERWOOD algorithm is based on the functional testing of over 250,000 shRNA sequences using a high-throughput sensor assay (Knott et al 2014) and uses key sequence characteristics for predicting shRNA potency to select the rare shRNA designs that are potent at single copy representation in the genome. The shERWOOD algorithm designs have been applied to the creation of shERWOOD-UltramiR shRNA collections targeting human, mouse and rat genomes.
- 1. shERWOOD algorithm designs – superior knockdown performance relative to existing shRNA design
- 2. UltramiR scaffold – increases shRNA processing and potency
- 3. All transcripts for a gene are targeted for the most complete knockdown
- 4. 100% Guaranteed* – Every shRNA is guaranteed to knockdown its intended target
Use the search tool to find and purchase lentiviral or retroviral shRNA targeting your gene of interest.
Following are the Lentiviral, inducible lentiviral and retroviral vector options with a choice of promoters for optimal expression in your target cell lines
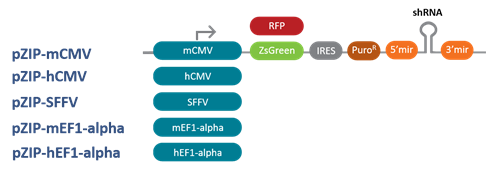
pZIP Lentiviral Vectors
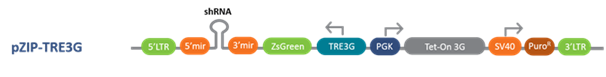
pZIP Inducible Lentiviral Vector
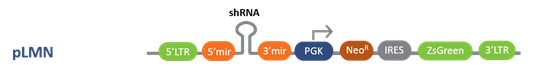
pLMN Retroviral Vector
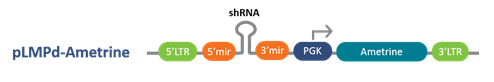
pLMPd-Ametrine Retroviral Vector
Supporting data
Superior Knockdown and Specificity with shERWOOD-UltramiR shRNA
shERWOOD-UltramiR shRNA designs are stringently selected by the shERWOOD algorithm and expressed from an optimized microRNA scaffold for increased small RNA processing. These designs outperform early generation shRNA libraries providing more efficient knockdown when compared at the individual gene level or in pooled shRNA screens. For details, please refer below publication.
A computational algorithm to predict shRNA potency (Molecular Cell. December 2014).
Design
shERWOOD-UltramiR shRNA Design
The shRNA-specific shERWOOD algorithm designs combined with an optimized UltramiR microRNA scaffold provide increased and consistent knockdown efficiency (Knott, et al., 2014). An unbiased screen (“Sensor Assay”) of 270,000 shRNA sequences was used to train the shERWOOD algorithm. Of these, only ~2% of the sequences tested showed extremely potent knockdown at single copy and this data set was used to train the shERWOOD algorithm. In addition, optimization of the microRNA scaffold provides increased microRNA processing.
Benefits of shERWOOD shRNA design algorithm:
- 1. The first shRNA-specific design algorithm
- 2. Optimized to predict designs based on potent single copy knockdown
- 3. Designs target all transcripts of the gene
- 4. Includes filters to minimize off target effects
Optimized scaffold for increased small RNA processing
Previous generation microRNA-adapted shRNA libraries have alterations in conserved regions of the mir-30 scaffold that were suboptimal for small RNA processing and consistency of knockdown. The alternate miR scaffold called UltramiR has been optimized based on recent knowledge of the key determinants for optimal primary microRNA processing (Auyeung et al. 2013). This new scaffold increases shRNA processing presumably by improving biogenesis. When shRNA were placed into the UltramiR scaffold, mature small RNA levels were increased roughly two fold relative to levels observed using the standard miR-30 scaffold (Knott et al., 2014).
Purchase
shERWOOD-UltramiR shRNA target human, mouse and rat genomes and are available as Target Gene Sets with the top 3 ranked shRNA targeting a gene of interest plus a non-targeting control.
| Product Formats |
Delivery Time |
| Glycerol stock: E. coli bacterial culture in LB-Lennox (low salt) broth with 8% glycerol |
3-4 weeks |
| Lentiviral particles, 1mL at >1 x 106 TU/mL |
4-5 weeks |
| High titer lentiviral particles, 100µL at > 1 x 108 TU/mL |
4-5 weeks |